Harnessing Stellar Power: The Promising Future of Fusion Energy
Written on
The Potential of Fusion Energy
Recent advancements in fusion energy have sparked excitement in the scientific community. Researchers at the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory have made a groundbreaking discovery: they successfully generated more energy from a fusion reaction than was consumed to initiate it. This pivotal moment signifies a major leap toward realizing clean energy, potentially allowing us to tap into the power of the stars within the next few decades, all while avoiding the challenges of managing radioactive waste. Unlike current fission reactors, which generate hazardous waste, fusion reactors promise a cleaner energy source that could significantly benefit our increasingly polluted planet.
As we explore the fundamental differences between fusion and fission, it’s crucial to understand that fission involves splitting atomic nuclei, releasing substantial energy that generates heat and drives turbines for electricity. However, this process is notorious for producing large amounts of radioactive waste, posing environmental risks.
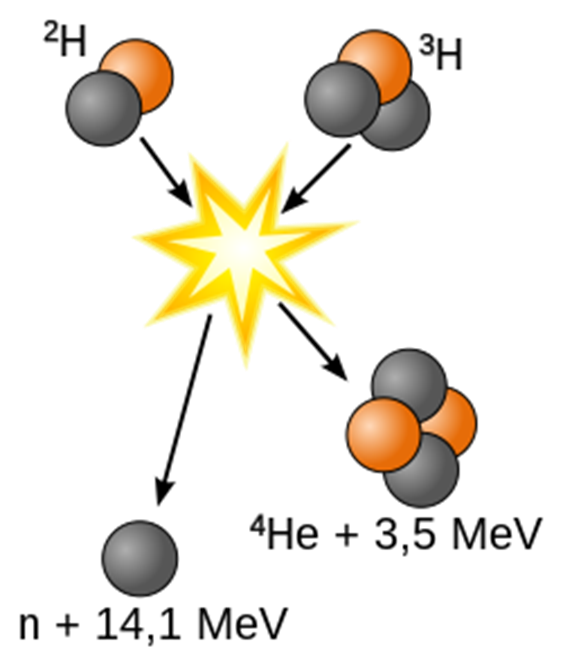
Fusion, on the other hand, entails merging two hydrogen atoms to form helium. This reaction releases energy and heat, which, similar to fission, can be harnessed for power generation. As noted in a recent article, “Fusion operates by compressing hydrogen atoms with such intensity that they merge into helium, unleashing significant energy and heat. Unlike other nuclear processes, it does not result in radioactive waste” (Fusion Energy).

The Implications for Energy and the Environment
The advent of fusion technology could render fossil fuels obsolete, eliminating our reliance on coal and natural gas for energy and heating. This transition could mark the end of an era plagued by smog and ozone depletion. However, the benefits of this technology extend beyond terrestrial applications.
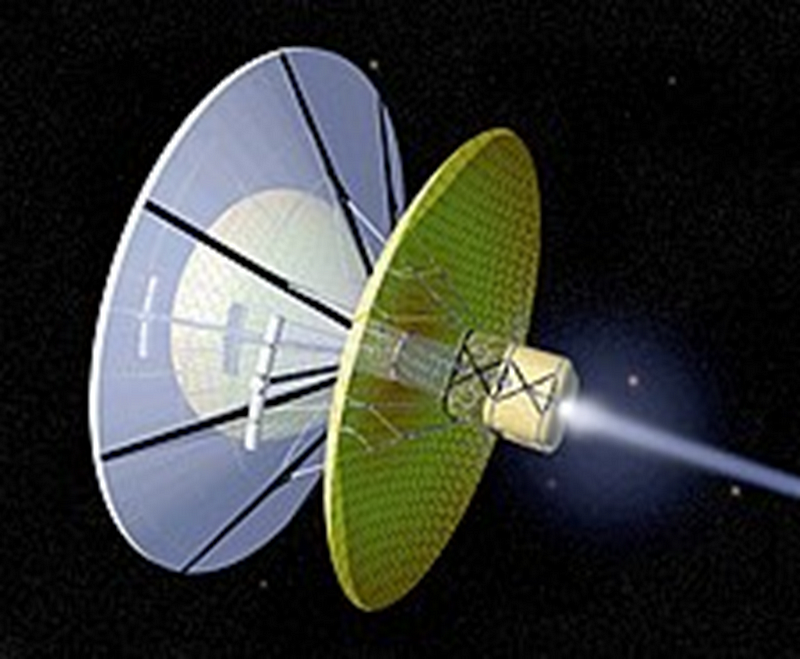
Space exploration is another arena where fusion energy could prove transformative. Numerous designs for fusion-powered spacecraft have been proposed, some of which would eject charged particles at high speeds to propel through space. Certain models even have the capability to collect helium-3 fuel during their journey. Such vessels could achieve velocities reaching thousands of kilometers per second. As Richard Hollingham describes, “A starship traveling at thousands of kilometers per second could reach Mars in weeks, traverse the outer solar system in months, and reach neighboring star systems in years” (Hollingham).
Challenges Ahead
Despite these promising developments, it is important to remain realistic. The recent breakthrough in energy production lasted only for a brief period, and we are still far from achieving a sustained, controlled fusion reaction. However, this experiment has validated the technology's potential and could pave the way for the first commercial fusion reactor in the next twenty to thirty years.
While many of us may not witness the full realization of the fusion dream, there is hope that future generations will benefit from its advancements. Unfortunately, older generations may have to content themselves with visions of a cleaner world, where the stars are within reach. It is my sincere wish that the future of fusion leads to exploration and discovery.
If you found this article interesting, consider following me on Medium to support my work. Thank you!
The first video titled "Is nuclear fusion the future of clean energy?" explores the transformative potential of fusion energy and its implications for sustainable power generation.
The second video, "The Future of Fusion Energy," discusses the advancements and challenges in fusion research and its potential to revolutionize energy production.