NASA's Mars 2020 Rover: SuperCam and Future Mission Insights
Written on
Chapter 1: The Mars 2020 Rover Takes Shape
NASA's Mars 2020 rover is gradually coming together. Following the integration of its stereoscopic navigation cameras and initial wheel prototypes, engineers at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) have now secured the SuperCam Mast Unit onto the rover. This crucial instrument will enable Mars 2020 to remotely analyze samples as it hunts for evidence of past life.
The SuperCam is positioned on one side of the mast unit. NASA has taken to personifying its robotic explorers with their numerous selfies, making it easy to view this as the rover's "head." While Curiosity features a similar mast design, its instrument is referred to as the ChemCam.
Curiosity's ChemCam employs laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) alongside a Remote Micro Imager (RMI) telescope. In contrast, the SuperCam represents a more sophisticated evolution of the ChemCam. It includes a LIMS, a Raman spectrophotometer, an infrared (IR) spectrophotometer, and a telephoto camera. This advanced tool is the result of collaboration among researchers from the US, France, and Spain. The last component, the IR spectrophotometer, recently arrived from France, completing the SuperCam's assembly.
NASA has indicated that the SuperCam will empower Mars 2020 to examine samples for life signs, even those that may have disappeared millions of years ago. Remarkably, the SuperCam can focus on a sample as small as a pencil point from over 20 feet (6 meters) away, reducing the need for frequent minor adjustments to the rover's position during sample analysis.
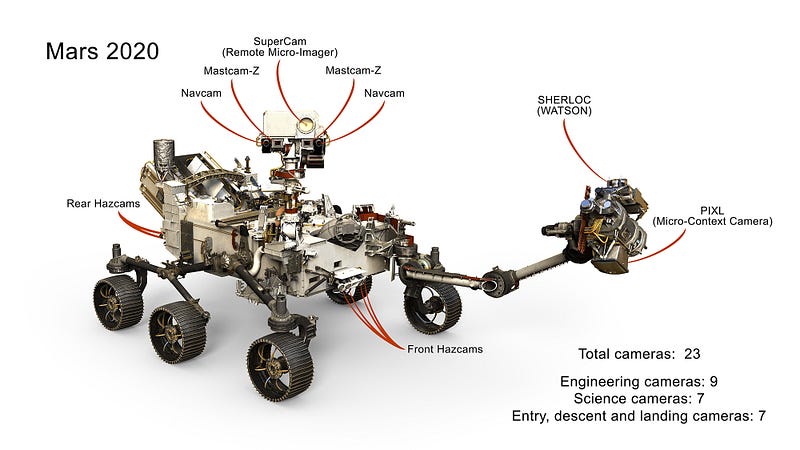
This rover will ultimately be equipped with 23 cameras by completion. Over the next few weeks, JPL engineers will implement the Mars 2020 Sample Caching System, which utilizes 17 motors to collect Martian soil samples for storage within the rover. Plans are in place for a potential future mission to retrieve these samples and bring them back to Earth.
NASA intends to launch Mars 2020 next summer, at which point it will receive its official name. The rover is set to land in Jezero Crater in February 2021, utilizing a rocket sled design similar to that of Curiosity. Once on Martian soil, Mars 2020 will be able to detect biosignatures that Curiosity might overlook. The mission is projected to last at least one Martian year, which is just under two Earth years, and if it mirrors Curiosity's longevity, it could function well beyond that timeframe.
This video provides an update on NASA's Perseverance Rover SuperCam instrument, detailing its capabilities and how it will aid in Mars exploration.
This video covers the countdown to Mars for NASA's Mars 2020 Perseverance Rover, highlighting mission objectives and preparation efforts.
Now read: NASA Sends Tiny Atomic Clock to Space and Get a Birds-Eye View of NASA’s Mars 2020 Rover Landing Zone.