Exploring Primitive Data Types and Variables in Java
Written on
Chapter 1: Understanding Data Types and Variables
In this tutorial, we will dissect the concepts of data types and variables in Java, explaining their fundamental roles. This guide incorporates programming terminology that may not be suited for beginners. Therefore, if you're new to coding, it may be better to look for introductory resources. However, for students preparing for exams or interviews, this information will be beneficial for your studies.
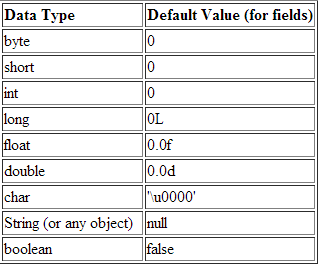
Fields vs. Local Variables
Fields

Local Variables
Local variables are defined within methods or code blocks. Unlike fields, they must be explicitly assigned a value upon declaration, as they cannot hold a static state. Failure to initialize a local variable before use will result in an undefined error in the console.
Chapter 2: The Distinction Between Primitive Types and Object References
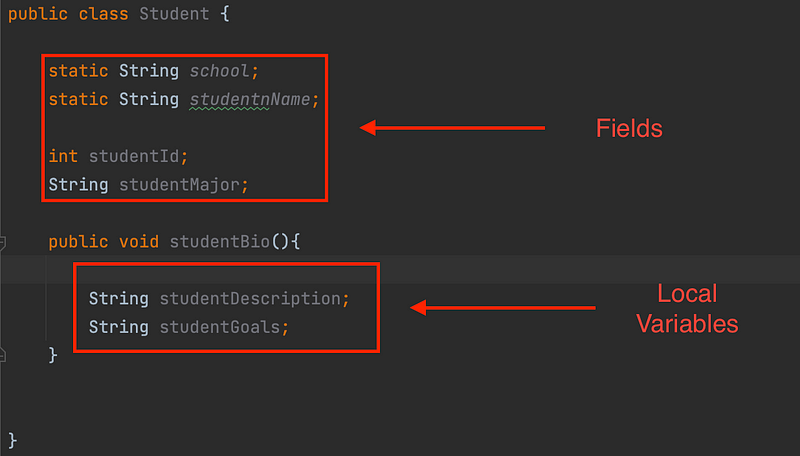
Primitive data types are designed to hold raw values and cannot represent null, while object references point to their values and can store null.
Primitive Integral Types
Integral types represent whole numbers and cannot be expressed in decimal form. They are initialized to zero by default. The integral types, ordered by size, include:
- Byte: Comprising 8 bits, it can store values from -128 to 127, suitable for memory-efficient storage.
- Short: At 16 bits, it holds values ranging from -32,768 to 32,767.
- Int: A 32-bit integer that can manage values from approximately -2.1 billion to 2.1 billion. However, due to its memory consumption, it may not always be the best choice.
- Long: The largest integral type at 64 bits, capable of holding values between -9.2 quintillion and 9.2 quintillion. Typically, longs are used for time measurements in milliseconds. When declaring a long value, append an “L” to the end (e.g., long bigNum = 9_233_186_123L).
Float and Double Primitives
Both float and double types allow for the storage of integral values and represent data in decimal form. They cover a wider range than integral types and round large output values to fit within display constraints.
- Float: A 32-bit representation must include “F” at the end of its value (e.g., float aFloat = 21.22f).
- Double: A 64-bit representation that does not require a trailing character.
The Char Primitive
The char data type is capable of holding a single character, such as char letter = 'B'. More technically, it is a 16-bit integral type, with values ranging from 0 to 65,535, and can also represent Unicode characters. For example, char letterA = 65 will output 'A' when printed.
I hope you found this information valuable! Feel free to leave any questions or comments, and I will respond as soon as possible.
Resources
Level Up Coding Community
The first video provides a comprehensive overview of primitive data types in Java, detailing their functions and uses.
The second video serves as an introductory tutorial on variables and data types for Java beginners, ideal for those new to programming.