Exploring the Future of Space Travel: Dilemmas and Opportunities
Written on
Chapter 1: The Impending End of the International Space Station
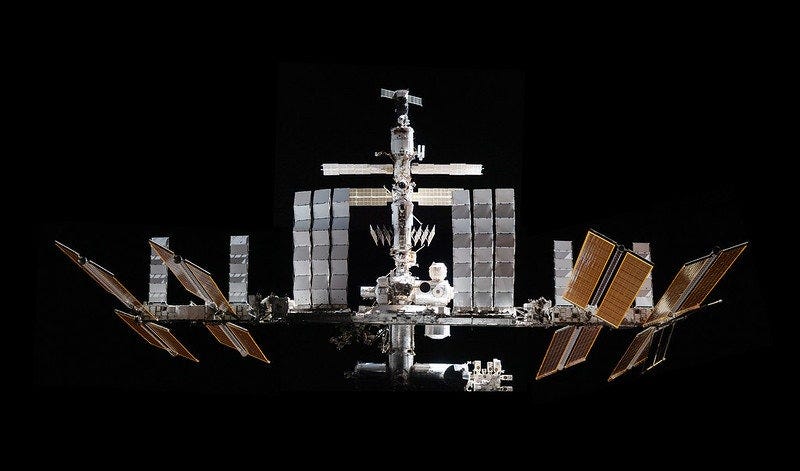
In the coming years, the International Space Station (ISS) is expected to face its demise, likely occurring suddenly due to a critical failure or structural breach. Astronauts may need to evacuate, and the ISS will inevitably descend to Earth, where it will disintegrate upon re-entry due to intense heat.
Having orbited the planet for over thirty years and costing around $150 billion, the ISS stands as humanity's most expensive construction. Its grandeur is reminiscent of ancient wonders like the Pyramids of Giza. However, unlike these enduring structures, the ISS cannot withstand the harsh conditions of space, which include radiation and debris. Initially, the ISS was expected to last about fifteen years, but it has exceeded those predictions, proving its resilience.
Nevertheless, this longevity may be its downfall. Many of its components were only designed for the initial projected lifespan, and extending their use could lead to catastrophic failures. The potential for upgrades or replacements was minimally considered, leaving some critical parts irreplaceable.
The first video discusses what the future of space travel may look like, featuring insights from Chris Impey. It explores both the challenges and advancements on the horizon.
Section 1.1: The Next Steps for Space Exploration
As we contemplate the future of space, it is crucial to consider what will replace the ISS. NASA currently seems more focused on lunar missions, proposing the Lunar Gateway as a smaller outpost for astronauts headed to the Moon.
China is also advancing its space endeavors, having launched the Tiangong space station. While it may not surpass the ISS in size, it could become the sole operational station by the 2030s. This scenario raises concerns among U.S. politicians, who worry about a "space station gap" that could diminish America's standing in space exploration.
Subsection 1.1.1: The Role of Private Sector in Space
In response, NASA is looking toward the private sector for solutions. By financially supporting companies like Axiom Space, NASA hopes to facilitate the construction of commercial space stations. This shift may lead to a new era of space exploration, allowing astronauts to conduct experiments in a more cost-effective manner.
Section 1.2: The Risks of Commercialization
While the rise of commercial space travel might promote innovation, it also raises ethical concerns. High-profile entrepreneurs like Elon Musk and Jeff Bezos are pushing forward ambitious projects, with Bezos even receiving funding from NASA for his space station project, Orbital Reef.
This concept envisions a space station functioning as a commercial hub, accommodating various guests, including tourists. Such developments could exacerbate societal inequalities, creating a divide between the wealthy elite who can afford space travel and the general public.
Chapter 2: Balancing Progress with Equity
The potential for commercial space stations is exciting, yet it poses significant risks. The public's support for space exploration is vital, and the focus on billionaire-led initiatives could undermine this. While billionaires have the resources to make significant advancements, their endeavors often highlight societal disparities.
The second video explores the new frontier of space travel, addressing the implications of private investments in space exploration and the future of human presence beyond Earth.
To ensure that space remains a domain for all humanity rather than a playground for the rich, a careful approach is necessary. NASA must strive to maintain the spirit of exploration for everyone, making sure that advancements in space are viewed as milestones for civilization rather than symbols of inequality.
If you found this discussion enlightening, consider subscribing for regular updates. Subscribers receive one to two emails each week, covering the latest developments in space and physics.